Class 9 Geography Chapter 10. Urbanisation/Textual Exercise /Questions and answers
Class 9 Geography
Chapter 10. Urbanisation/Textual Exercise /Questions and answers
Q 1. Suggest measures for the following problems:
(A) The slums in the cities are increasing.
Ans:
1.Creating more job opportunities in the rural areas so that migration is minimised.
2.Poverty alleviation schemes need to be implemented to improve the standard of living of the poor.
3.Initiative for improvement of sanitation, housing and other facilities must be facilitated.
(B) Because of the increasing traffic jams within the city, lot of time is consumed in commuting.
Ans: 1.To reduce traffic jams, carpooling is a great way to get to and fro work.
2.Planning the route in advance will help to avoid any road construction or other traffic jams.
3.Making use of public transportation like Railways, BEST, etc. will also help in reducing traffic congestion and precious fuel.
(C) The question of law and order in the urban areas is serious.
Ans: 1.Many crimes are due to poverty and unemployment. Poverty alleviation and employment generation programmes should be given priority.
2.The semi-literate / educated unemployed persons should be given skill-training and be prepared for self-employment.
3.The police and the judicial system “should be strengthened to wipe out criminals.
(D) The problem of pollution is grave because of urbanisation.
Ans: 1.Walking or cycling to the work place will not only help in improving the health conditions of individuals but will also help in reducing pollution.
2.Cities need to green up (plant more trees) as trees are considered to be the natural purifiers.
3.Strict action should be taken against polluting industrial units.
(E) Migration has created questions of health and education in urban areas.
Ans: 1.Migration from rural to urban areas can be reduced if employment opportunities are provided in the rural areas.
2.Infrastructure like transport, electricity, public distribution system, etc. need to be provided in the rural areas.
3.Educational institutes and health centres need to be upgraded in the rural areas.
Q 2. Match the correct pairs :
(1) Technological development and mechanization – (D) Urbanisation
(2) Permanently staying away from your original place – (C) Migration
(3) 75% males are engaged in non-agricultural occupation – (A) Urban areas
(4) The problems of solid waste – (B) Lack of planning
Q 3. Outline the importance/ advantages of the following:
(A) Technology and mechanisation
Ans:
1.Technology and mechanisation increase industrial production, creates employment and is useful for urbanisation.
2.In recent decades, the use of technology and mechanisation has increased in agriculture.
3.Due to the mechanisation of agriculture, the surplus manpower employed in agriculture have become devoid of agricultural work.
4.This working class started coming to cities to look for work and as a result urban population started increasing.
(B) Trade
Answer:
1.When a place in a region is favourable in terms of transport, loading-unloading and storage of goods, it developes into a trade centre.
2.This leads to the growth of business complexes, banks, credit societies, godowns, cold storage, houses, etc.
3.For example, Nagpur’s central location has facilitated trade and hence urbanisation has also taken place here.
(C) Industrialisation
Answer:
1.Industrialisation leads to increase in the hopes of people who are attracted towards the industries from surrounding areas for employment.
2.Rapid growth of Mumbai in the 19th century was due to the textile mills which were started here.
3.Many fishing villages (Koliwadas) became part of Mumbai metropolitan2 area due to industrialisation and urbanisation.
D)Amenities in urban areas
Answer:
1.Urbanisation leads to development of a number of amenities and facilities in urban areas.
2.Transportation, communication, educational facilities, medical facilities, fire brigade, various sources of entertainment, etc. are examples of amenities in urban areas.
3.A good transportation not only makes a journey easier but also has a positive effect on freight transport, development of markets, trade, etc.
4.Development of higher educational facilities in urban areas attract students from rural areas to urban areas. E.g. Pune.
5.Development of high quality medical facilities in urban areas bring many patients and their family members from different parts of India to these areas.
(E) Social harmony in the cities
Answer:
1.Social harmony refers to the exchange of cultural and social customs and traditions as people from different parts live together in the cities.
2.An increase in urbanisation leads to an increase in secondary, tertiary and quaternary occupation.
3.This results in an increase in employment opportunities due to which people from different parts of the country come to cities and there is an exchange of customs and traditions.
Q 4. Compare the following and give examples:
(A) Transportation system and traffic jams
Ans:
1.As cities grow, people start living on the outskirts and in the suburbs of the city.
People commute to the centre of the city for businesses and industries, trade, jobs, education, etc.
2.Public transportation system is insufficient and hence the number of private vehicles increase.
3.This results in an increase in traffic jams and a lot of time is consumed in travelling from one place to another.
4.e.g. Although Mumbai has a well developed transportation system it is insufficient to fulfil the growing needs of people.
Hence, traffic jams are a frequent site in different pockets of Mumbai.
(B) Industrialisation and air pollution
Answer:
1.Industrialisation refers to the growth in number of industries in a particular region.
As more and more industries crop up, it becomes convenient for the industries to violate the environmental laws.
2.Paucity of facilities, insensitivity towards environment are the other factors which leads to an increase in the pollution level.
3.Hence, Industrialisation and Air pollution are the two aspects of the same coin.
4.e.g. Delhi, Faridabad and Varanasi are the ! victims of rapid industrialisation leading to j severe air pollution.
(C) Migration and slums
Answer:
1.The increase in the number of migratory people causes an increase in the slums.
2.Generally migration from rural to urban areas takes place in search of job opportunities, which are hard to find.
3.The housing facilities do not increase in the same proportion as the population, so the poor migrants can not afford the housing in the cities.
4.This encourages the migrants to build illegal temporary and semi-structured houses known as slums, in open spaces. 5.e.g. Slums in Dharavi (Mumbai city)
(D) Amenities and increasing crime
Answer:
1.Amenities refers to facilities that provide comfort, convenience or pleasure to people.
2.Transportation, communication, educational and medical facilities, fire brigade, etc. are the examples of amenities available in urban areas.
3.Unemployed people who have migrated to the cities are unable to avail these amenities.
4.This leads to an increase in thefts, burglaries, scuffles5, murders, etc. which disturb the social harmony of the cities.
5.e.g. Pick pocketing in the local trains.
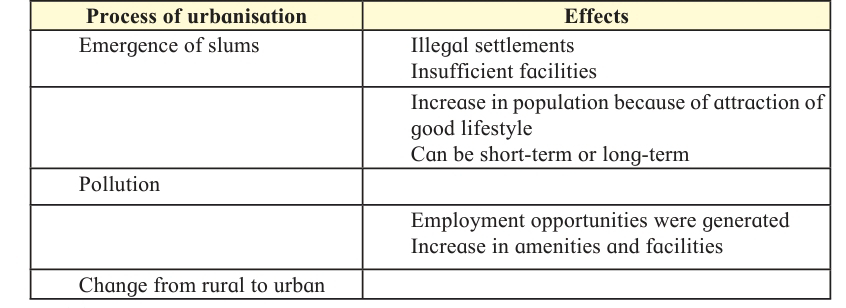
Q 5. Complete the table :
(A) The growth of cities takes place in a specific method.
Answer:
1.Villages are transforming into cities. The growth of cities take place in a particular pattern.
2.At first various industries like factories, mills, energy plants, multi-purpose projects3 etc., come up in rural areas.
3.People from surrounding areas come to work here and the population of the village increases.
4.To fulfill their needs other services develop like medical facilities, food, hospitals, recreation, etc.
5.The Gram Panchayat gives way to a Municipal Corporation.
6.These bodies provide basic services to citizens like drinking water, roads, transportation, sewerage network, street lighting etc.
7.Other facilities develop like town planning recreation facilities, tourist places, parks etc.
(B) A planned city of your imagination
Answer:
1.A city which is carefully planned from its inception and is constructed in a previously undeveloped area is a planned city.
2.A planned city is one in which there is adequate infrastructural facilities like roads, railways, water supply, power supply, etc.
3.Also, there should be open spaces available for recreation facilities.
(C) Industrialisation causes cities to develop.
Answer:
1.The development and concentration of industries in a region is a factor contributing towards urbanisation.
2.Increase in industries leads to increase in the hopes of people who are attracted towards these industries from surrounding areas.
3.An increase in population leads to the development of infrastructural facilities like roadways, railways, power supply, water supply etc. which are the characteristics of a planned city.
4.In the 19th century, Mumbai grew rapidly because textile mills started on a large scale.
(D) Pollution- A problem
Answer:
1.Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into natural environment that causes adverse changes.
2.Pollution can be that of air, water, noise, solid waste, etc.
3.Pollution can adversely affect the human health.
4.Water pollution can lead to several water borne diseases like typhoid, cholera etc. Air pollution can lead to asthma and other respiratory diseases. Noise pollution can lead to sleep disturbance, hearing impairment etc.
(E) Swachchh Bharat Abhiyan
Answer:
1.Swatch Bharat Abhiyan is a cleanliness campaign run by the Government of India.
‘One step towards cleanliness’ is the objective of this campaign.
2.This campaign aims to keep the streets and infrastructure of the country’s cities, towns and its rural areas clean.
3.The funds for this programs are raised by ‘Swachchh Bharat Cess’.



Comments
Post a Comment