Class 9 Geography 5.Precipitation /Exercise /questions and answers/ maharashtr boad/ssc board
Class 9 Grography
5. Precipitation
Q1. Identify the precipitation type with the help of the description given:
(a) It is the main source of the water that
you use. Sometimes it is torrential and
sometimes continuous. Most of the
agriculture in India is dependent on it.
Ans: Rainfall
(b) It seems as if water droplets are
floating in the atmosphere. In London,
one cannot see the Sun till the
afternoon during winters because of
this phenomenon.
Ans: fog
(c) It never precipitates like this in
equatorial areas. Precipitation in the
solid form sometimes causes damage to the crops.
Ans: Hail
(d) A white cotton like layer spreads on the
earth’s surface. Because of this form of
precipitation, the State of Jammu and
Kashmir has to change its capital in
winters. In Maharashtra, it does not
precipitate like this.
Ans: snow
Q2 Look at the following pictures and identify the correct rainfall type.
Ans: Conventional Rain Fall.
Ans: Orographic rainfall.
Ans: Cyclonic rainfall.
Q 3. Look at the figures above and answer the following questions:
(1) In fig B, on which side of the mountain
is it raining more?
Ans: The windward side is receiving more rainfall.
(2) Shade the rain shadow region in fig B
and name it.
Ans: Students to show the leeward side in the picture.
(3) What is the difference between A and C?
Answer:In figure 5.4 i.e. convectional rainfall the hot air rises upwards and then the air cools and begins to condense and due to continuous condensation rainfall occurs. Here rainfall is accompanied by lightning and thunder.
In figure 5.6 , i.e. cyclonic rainfall, air from surrounding regions comes towards the centre of the cyclone and starts moving upwards. As it rises, the temperature of the air reduces, condensation occurs and rainfall takes place.
(4) Stormy winds and floods are associated
with which rainfall type?
Ans: Stormy winds and floods are associated with Cyclonic rainfall
(5) What type of rainfall occurs in Singapore?
Ans: Cyclonic rainfall occurs in Singapore.
Q 4. Identify the odd man out :
(1) Orographic rainfall, acid rain, cyclonic
rainfall, convectional rainfall
Ans: Acid rainfall
(2) Snowfall, rainfall, hailstones, dew
Ans: Dew
(3) Thermometer, rain gauge, anemometer,
measuring jar
Ans: Measuring jar
Q 5. Answer in brief:
(1) In what ways does precipitation occur
on the earth?
Answer:Precipitation means water falls in the solid or liquid state from the clouds to the earth surface. Snow, hailstorms, rainfall are the major forms of precipitation.
(2) Comment on the rainfall occuring in
the rain shadow area.
Answer:
The winds coming from lakes or seas are moisture-laden and they are obstructed by the high mountain ranges coming in their way
They start going upwards along the slope of the moutains. The temperature of these winds drop and condensation occurs and rainfall takes place.
This rainfall takes place because of the obstruction of the mountains which results in the condensation of water vapour.
The windward side of the mountain gets more rain; the amount of vapour in the air reduces after crossing the mountain and the moisture-holding capacity of the air increases.
The leeward side of the mountain gets lesser rainfall as compared to windward side.
Thus, the leeward side area is identified as rain shadow area as it recieves meagre rainfall.
(3) Which type of rainfall occurs in most of
the world? Why?
Answer:
Orographic rainfall occurs in most parts of the world.
Convectional rainfall is regional in nature.
There is a certainty in the convectional rainfall occurring in the equatorial areas.
Comparatively, the orographic and cyclonic rainfall is less certain.
And therefore, such areas are prone to very heavy rainfall, floods or droughts frequently
(4) If condensation occurs closer to the
earth’s surface, what types of forms
become visible?
Answer:
If condensation and solidification of the water vapour in the atmosphere closer to the earth surface are visible, they are in the form of fog, dew or frost.
(i) Fog:
The temperature of the layers of the air near the surface of the earth reduces. As the temperature reduces, water vapour condenses.
In this process the water vapour turns into microscopic water particles and float in the air.
When the density of these droplets in the air increases it leads to the formation of fog
(ii) Dew:
When moisture-laden air near the earth surface comes in contact with very cold objects condensation of water vapour takes place.
They turn into very small water droplets and stick to the surface of cold objects, e.g. eg: leaves and this is called dew.
(iii) Frost:
When the temperature of the air reaches less then 0 degree Celcius the water droplet stuck to the surface of the cold objects and freezes.
This frozen water droplet is called as frost.
(5) What precautions should be taken while measuring rainfall?
Ans: Rainfall is an important source of water on planet earth and rainfall is formed because of changes in the temperature of the air with water vapour.
The instrument that is used to measure rainfall is called rain gauge.
The funnel i.e. used for measuring rain has a specific diameter and the rain falling in this funnel is collected in bottle fitted in the gauge.
The collected water is then measured with the help of measuring jar. In the areas of heavy rainfall, the reading of the rain with rain gauge should be taken every three hours. The measuring jar reads rain in millimetres
The gauge has to be kept on open ground on 30cm high flat-mount.
So that the rain water is collected without any obstruction.
Q 6. Distinguish between -
1.Dew and frost
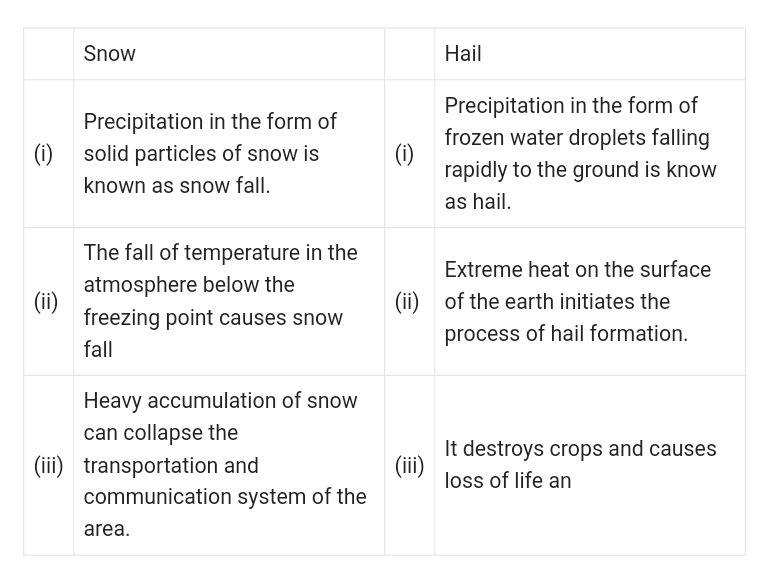
(2) Snow and hail
Study the rainfall map of the world given in Fig 5.7 carefully and answer the following questions:(Page No 47)
1.Which region experiences more rainfall?
Ans: The tropical region experiences more rainfall.
2.What is the reason for low rainfall in the central Peninsular India?
Ans: The Central Peninsular India falls on the leeward side of the Western Ghats and hence a rain shadow region is formed here.
3. Why does the eastern part of central African Continent gets less rainfall than the western part despite its location close to the equator.
Ans:Eastern part of the African Continent is a rain shadow region of westerly monsoon winds whereas the western part lies on the windward side and gets more rain.
The eastern part of Africa also comes under the influence of the North east trade winds but still receive less rains as they are dry winds originating from the land.
4.Why does the amount of high rainfall in the western part of the European continent reduces in the eastern part?
Ans:There are many mountain ranges in the western part of Europe. These obstruct the rain-bearing clouds coming from the west and therefore the amount of rainfall received is high in the west and it reduces towards the east.
5. Why is the rainfall more only in the eastern coast of Australia?
Ans:The eastern part of Australia is a mountainous region. The winds blowing from the Pacific Ocean are obstructed by these mountains resulting in orographic rainfall towards the east and the formation of a rain shadow zone towards the west.







Comments
Post a Comment