REVISION QUESTION- BANKClass 8 Subject: History and Civics
REVISION QUESTION- BANK
Class 8 Subject: History and Civics
Q.1. Fill in the blanks.
1.The ......... is a museum in Pune which gives information about the history of Mahatma Gandhi.
Ans: Aga Khan Palace
2. A unique discovery of modern technology in 20th century is .......
Ans; Films
3 ............ wrote the Geeta Rahasya.
Ans: Lokmanya Tilak
4.The Ottoman Turks conquered............. which was the Byzantine Empire.
Ans; Constantinople
5. As a protest to Jallianwala Baug massacre, Rabindranath Tagore returned the title of ......... bestowed upon him by the British Government.
Ans: Sir
6. Portuguese,.........., French, British participated in competition of capturing Indian Market.
Ans: Dutch.
7. The Industrial Revolution began in .......
Ans: England
8. V.D. Davarkar named the struggle of 1857 as .....
Ans: Indian war of Independence
9. .......... was the Governor General who annexed the princely states.
Ans: Lord Dalhousie
10. Jamshedjee Tata started the manufacturing of steel at Tata Iron and steel industry established in ........
Ans: Jamshedpur
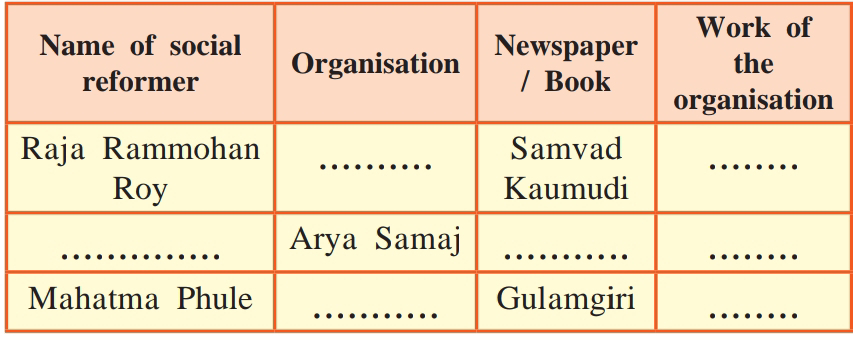
Q.2. Complete the chart.
1.2.Classify the following leaders in the Moderate phase and Extremist phase.
( Gopal Krishna Gokhale, Lokmanya Tilak, Ferozshah Mehta, Lala Lajpat Rai, Surendranath Banerjee, Bipin Chandra Pal ).
Class 8 Subject: History and Civics
Q.1. Fill in the blanks.
1.The ......... is a museum in Pune which gives information about the history of Mahatma Gandhi.
Ans: Aga Khan Palace
2. A unique discovery of modern technology in 20th century is .......
Ans; Films
3 ............ wrote the Geeta Rahasya.
Ans: Lokmanya Tilak
4.The Ottoman Turks conquered............. which was the Byzantine Empire.
Ans; Constantinople
5. As a protest to Jallianwala Baug massacre, Rabindranath Tagore returned the title of ......... bestowed upon him by the British Government.
Ans: Sir
6. Portuguese,.........., French, British participated in competition of capturing Indian Market.
Ans: Dutch.
7. The Industrial Revolution began in .......
Ans: England
8. V.D. Davarkar named the struggle of 1857 as .....
Ans: Indian war of Independence
9. .......... was the Governor General who annexed the princely states.
Ans: Lord Dalhousie
10. Jamshedjee Tata started the manufacturing of steel at Tata Iron and steel industry established in ........
Ans: Jamshedpur
Q.2. Complete the chart.
1.2.Classify the following leaders in the Moderate phase and Extremist phase.
( Gopal Krishna Gokhale, Lokmanya Tilak, Ferozshah Mehta, Lala Lajpat Rai, Surendranath Banerjee, Bipin Chandra Pal ).
Moderate Phase Extremist phase
1 Gopal Krishna Gokhale 1. Lokmanya Tilak
2 Ferozahah Mehta 2. Lala Lajpatrai
3 Surendranath Banarjee 3. Bipin Chandra Pal
3.Complete the table.
Q.3. Answer the following in one sentence.
1. Who did start the fortnightly 'Mooknayak'.
Ans: Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar started the fortnightly 'Mooknayak'.
2.Which are the historical sources based on Modern technology?
Ans: The art of Photography, recording, Films etc are the historical sources based on Modern technology.
3.What is powada?
Ans: Powada is a source of getting information about a historical event or the work of a person.
4. Where did Gandhiji launch the first satyagraha in India?
Ans: Gandhiji launched the first satyagraha in Champaran in India.
5.Who was responsible for the Jallianwala Baug Massacre?
Ans: General Michael O'Dwyer, Governor of Punjab was responsible for the Jallianwala Baug Massacre.
6. Who did introduce civil services in India?
Ans: Lord Cornwallis introduced civil services in India.
7.What is Dual Government?
Ans: The company undertook the work of revenue collection wheras the Nawab of Bengal had to maintain law and order.
8.Who has manage to sail past the Cape of Good Hope and reached the Indian Coast in Calicut.
Ans: Vasco-da-gama has manage to sail past the Cape of Good Hope and reached the Indian Coast in Calicut.
Q. 4. Give reasons.
1.Farmers in India became bankrupt.
Ans: Following are the reasons:
1. Payment of tax was made compulsory in the form of cash.
2. If the farmer failed to pay tax in time, then his land would be confiscated.
3. At a certain times the farmer had to mortgage his land to the money lender for arrangement of money to pay the tax.
Hence the farmer became bankrupt.
2.There was decline of traditional industries in India.
Ans:
1. The British government obtained huge taxes on exported goods from India to England.
2. Very less tax was imposed on the imported goods from England.
3. The goods manufactured in England were machine made so maximum production at minimum cost.
4. The Indian artisan failed to compete with them so it led to closing down of the traditional industries.
3.In the struggle for independence, a sense of identify was awakened among the Indians.
• Ans: Western education familiarised the educated Indians with modern values such as liberty, equality, democracy and nationalism.
• The Asiatic Society at Bengal edited and published hundreds of manuscripts in Sanskrit, Persian and other Indian languages.
• The realization that India had a rich ancient heritage aroused the feeling of national pride. This gave a sense of identity to Indians.
4.Lord Curzon decided to partition Bengal.
Answer:
1. Bengal was a large province. So under the pretext of administrative convenience, the province of Bengal was partitioned by Lord Curzon.
2. Accordingly, the Muslim-majority East Bengal and the Hindu-Majority West Bengal were created in 1905.
3. The real motive was to create a divide between the Hindus and the Muslims and thereby weaken the nationalist movement. The British used the Policy of ‘Divide and Rule’.
5. Gandhiji suspended the Non-co-operation Movement.
• Ans: In February, 1922 the police opened fire on a peaceful procession at Chauri-Chaura in Gorakhpur district of Uttar Pradesh.
• In retaliation to this, the enraged mob set fire the police station in Chauri- Chaura.
• Twenty-two policemen including one officer were killed in this incident.
• Gandhiji was hurt by this incident. So he decided to suspend the Non-co-operation Movement on 12 February, 1922.
6. The Indians boycotted the Simon
CIVICS
Q.1. Rewrite the statements by choosing the appropriate options.
1. Parliamentary System of government
developed in ............. .
(a) England (b) France
(c) United States of America (d) Nepal
Ans; Parliamentary System of government
developed in England.
2. In the Presidential system ............ is the
executive head.
(a) The Prime Minister
(b) The Lok Sabha Speaker
(c) The President (d) The Governor
Ans: In the Presidential system the president is the
executive head.
3. The tenure of the President is of ...... years. (three, four, five)
Ans; The tenure of the President is of 05 years.
4. In India, the executive power is vested
with the …………… .
(President, Prime Minister, Speaker)
Ans; In India, the executive power is vested
with the President.
5. As per the constitution there can be a maximum of ...... members in the Lok Sabha.(525, 552,545)
Ans; As per the constitution there can be a maximum of 552 members in the Lok Sabha.
6. India’s ............. is the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha.
(a) President (b) Vice-President
(c) Prime Minister (d) Chief Justice
Ans: India’s Vice-President is the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha.
7. In the Parliamentary form of government, the .........is a supreme institution. (Executive, Judiciary, Legislature)
Ans: In the Parliamentary form of government, the Executive a supreme institution.
8. The .......... leads the Council of Ministers.(President, Prime Minister, Lok Sabha speaker)
Ans: The Prime Minister leads the Council of Ministers.
Q.2. Complete the chart
1.
1 Gopal Krishna Gokhale 1. Lokmanya Tilak
2 Ferozahah Mehta 2. Lala Lajpatrai
3 Surendranath Banarjee 3. Bipin Chandra Pal
3.Complete the table.
Q.3. Answer the following in one sentence.
1. Who did start the fortnightly 'Mooknayak'.
Ans: Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar started the fortnightly 'Mooknayak'.
2.Which are the historical sources based on Modern technology?
Ans: The art of Photography, recording, Films etc are the historical sources based on Modern technology.
3.What is powada?
Ans: Powada is a source of getting information about a historical event or the work of a person.
4. Where did Gandhiji launch the first satyagraha in India?
Ans: Gandhiji launched the first satyagraha in Champaran in India.
5.Who was responsible for the Jallianwala Baug Massacre?
Ans: General Michael O'Dwyer, Governor of Punjab was responsible for the Jallianwala Baug Massacre.
6. Who did introduce civil services in India?
Ans: Lord Cornwallis introduced civil services in India.
7.What is Dual Government?
Ans: The company undertook the work of revenue collection wheras the Nawab of Bengal had to maintain law and order.
8.Who has manage to sail past the Cape of Good Hope and reached the Indian Coast in Calicut.
Ans: Vasco-da-gama has manage to sail past the Cape of Good Hope and reached the Indian Coast in Calicut.
Q. 4. Give reasons.
1.Farmers in India became bankrupt.
Ans: Following are the reasons:
1. Payment of tax was made compulsory in the form of cash.
2. If the farmer failed to pay tax in time, then his land would be confiscated.
3. At a certain times the farmer had to mortgage his land to the money lender for arrangement of money to pay the tax.
Hence the farmer became bankrupt.
2.There was decline of traditional industries in India.
Ans:
1. The British government obtained huge taxes on exported goods from India to England.
2. Very less tax was imposed on the imported goods from England.
3. The goods manufactured in England were machine made so maximum production at minimum cost.
4. The Indian artisan failed to compete with them so it led to closing down of the traditional industries.
3.In the struggle for independence, a sense of identify was awakened among the Indians.
• Ans: Western education familiarised the educated Indians with modern values such as liberty, equality, democracy and nationalism.
• The Asiatic Society at Bengal edited and published hundreds of manuscripts in Sanskrit, Persian and other Indian languages.
• The realization that India had a rich ancient heritage aroused the feeling of national pride. This gave a sense of identity to Indians.
4.Lord Curzon decided to partition Bengal.
Answer:
1. Bengal was a large province. So under the pretext of administrative convenience, the province of Bengal was partitioned by Lord Curzon.
2. Accordingly, the Muslim-majority East Bengal and the Hindu-Majority West Bengal were created in 1905.
3. The real motive was to create a divide between the Hindus and the Muslims and thereby weaken the nationalist movement. The British used the Policy of ‘Divide and Rule’.
5. Gandhiji suspended the Non-co-operation Movement.
• Ans: In February, 1922 the police opened fire on a peaceful procession at Chauri-Chaura in Gorakhpur district of Uttar Pradesh.
• In retaliation to this, the enraged mob set fire the police station in Chauri- Chaura.
• Twenty-two policemen including one officer were killed in this incident.
• Gandhiji was hurt by this incident. So he decided to suspend the Non-co-operation Movement on 12 February, 1922.
6. The Indians boycotted the Simon
Commission.
Answer:
• The reforms introduced by Montague Chelmsford Act of 1919 was unsatisfactory.
• It created discontent among IndiAnswer: The British Government appointed the Simon Commission under the chairmanship of Sir John Simon in 1927.’
• There was not a single Indian member on the commission. In protest of this, the Congress boycotted the Simon Commission.
3.Why were the the sentiments of Hindu and Muslim hurt?
Ans; In 1856, the
British provided long range enfield rifles to the Indian sepoys. The sepoys were required to bite the end of the cartridges. The news spread out that these cartridges were smeared in the fats of cow and pig. Due to this the religious sentiments of
Hindu and Muslim sepoys were hurt and made them unhappy.
Answer:
• The reforms introduced by Montague Chelmsford Act of 1919 was unsatisfactory.
• It created discontent among IndiAnswer: The British Government appointed the Simon Commission under the chairmanship of Sir John Simon in 1927.’
• There was not a single Indian member on the commission. In protest of this, the Congress boycotted the Simon Commission.
3.Why were the the sentiments of Hindu and Muslim hurt?
Ans; In 1856, the
British provided long range enfield rifles to the Indian sepoys. The sepoys were required to bite the end of the cartridges. The news spread out that these cartridges were smeared in the fats of cow and pig. Due to this the religious sentiments of
Hindu and Muslim sepoys were hurt and made them unhappy.
CIVICS
Q.1. Rewrite the statements by choosing the appropriate options.
1. Parliamentary System of government
developed in ............. .
(a) England (b) France
(c) United States of America (d) Nepal
Ans; Parliamentary System of government
developed in England.
2. In the Presidential system ............ is the
executive head.
(a) The Prime Minister
(b) The Lok Sabha Speaker
(c) The President (d) The Governor
Ans: In the Presidential system the president is the
executive head.
3. The tenure of the President is of ...... years. (three, four, five)
Ans; The tenure of the President is of 05 years.
4. In India, the executive power is vested
with the …………… .
(President, Prime Minister, Speaker)
Ans; In India, the executive power is vested
with the President.
5. As per the constitution there can be a maximum of ...... members in the Lok Sabha.(525, 552,545)
Ans; As per the constitution there can be a maximum of 552 members in the Lok Sabha.
6. India’s ............. is the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha.
(a) President (b) Vice-President
(c) Prime Minister (d) Chief Justice
Ans: India’s Vice-President is the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha.
7. In the Parliamentary form of government, the .........is a supreme institution. (Executive, Judiciary, Legislature)
Ans: In the Parliamentary form of government, the Executive a supreme institution.
8. The .......... leads the Council of Ministers.(President, Prime Minister, Lok Sabha speaker)
Ans: The Prime Minister leads the Council of Ministers.
Q.2. Complete the chart
1.
Q.3 Answer im brief.
1. Enumerate the function of the Council of Ministers.
Ans: The functions of the Council of Ministers are as follows:
1. The Council of Ministers takes initiative in the process of Law-making by drafting the bills/proposals.
2. It introduces and discusses the bills/ proposals in the House.
3. It introduces bills on various subjects like education, agriculture, industry, health, foreign relations, etc. in the Parliament, conducts discussions on them and tries to get them approved by the Parliament.
4. It also takes the responsibility of implementing the policies approved by the Parliament.
2. How does the Parliament keep a check on the Council of Ministers ?
Ans: The Parliament keeps a check on the Executive in the following ways:
1. The bills/proposals presented by the Council of Ministers are discussed in the Parliament.
2. These discussions and debates help the members to scrutinize the bills/ proposals and point out the shortcomings and help in a creation of healthy laws.
3. During Parliamentary sessions, the proceedings of the House begins with questions asked by the members of the House. The concerned Ministers are expected to give satisfactory answers to these questions.
4. During the Parliamentary sessions, the period around 12 noon is called as ‘Zero House’. During this period, any question of public importance can be raised and discussed.
5. . The Parliament can pass a No-confidence motion on the Executive. If the motion is passed with majority support, then it has to resign.
3. Rajy Sabha is a permanent house. Explain it.
Ans: The upper and the second house of Parliament is the Rajya Sabha. The members of Rajya Sabha are indirectly elected. The Rajya Sabha gives
representation to 28 states and 9 Union territories in India. Thus, members of Rajya Sabha work as representatives of the constituent state.
3. Why is the role of opposition parties important.
Ans: Opposition parties may support the government wherever appropriate, point out
shortcomings in policies and laws, put up
studied arguments and questions etc. This
helps the legislature to make proper laws.
1. Enumerate the function of the Council of Ministers.
Ans: The functions of the Council of Ministers are as follows:
1. The Council of Ministers takes initiative in the process of Law-making by drafting the bills/proposals.
2. It introduces and discusses the bills/ proposals in the House.
3. It introduces bills on various subjects like education, agriculture, industry, health, foreign relations, etc. in the Parliament, conducts discussions on them and tries to get them approved by the Parliament.
4. It also takes the responsibility of implementing the policies approved by the Parliament.
2. How does the Parliament keep a check on the Council of Ministers ?
Ans: The Parliament keeps a check on the Executive in the following ways:
1. The bills/proposals presented by the Council of Ministers are discussed in the Parliament.
2. These discussions and debates help the members to scrutinize the bills/ proposals and point out the shortcomings and help in a creation of healthy laws.
3. During Parliamentary sessions, the proceedings of the House begins with questions asked by the members of the House. The concerned Ministers are expected to give satisfactory answers to these questions.
4. During the Parliamentary sessions, the period around 12 noon is called as ‘Zero House’. During this period, any question of public importance can be raised and discussed.
5. . The Parliament can pass a No-confidence motion on the Executive. If the motion is passed with majority support, then it has to resign.
3. Rajy Sabha is a permanent house. Explain it.
Ans: The upper and the second house of Parliament is the Rajya Sabha. The members of Rajya Sabha are indirectly elected. The Rajya Sabha gives
representation to 28 states and 9 Union territories in India. Thus, members of Rajya Sabha work as representatives of the constituent state.
3. Why is the role of opposition parties important.
Ans: Opposition parties may support the government wherever appropriate, point out
shortcomings in policies and laws, put up
studied arguments and questions etc. This
helps the legislature to make proper laws.







Comments
Post a Comment